I’m sure you’ve noticed that some speakers have dull black magnets, while others have shiny silver ones. That’s weird, right? Let me explain. The black ones are actually ferrite magnets, while the silver ones are neodymium-iron-boron magnets. What is the exact difference?So, what’s different about these two types of magnets? Which one is better? And how to choose when buying a speaker? Let’s learn about it today!
Ferrite VS NdFeB
Appearance
Ferrite is one of the more common magnetic materials that has no metallic luster and is usually not galvanized, so it usually appears matte black. In contrast, NdFeB is usually galvanized, which is primarily for corrosion protection, and due to the external manifestation properties of galvanizing, it gives it an attractive silvery-white metallic luster!
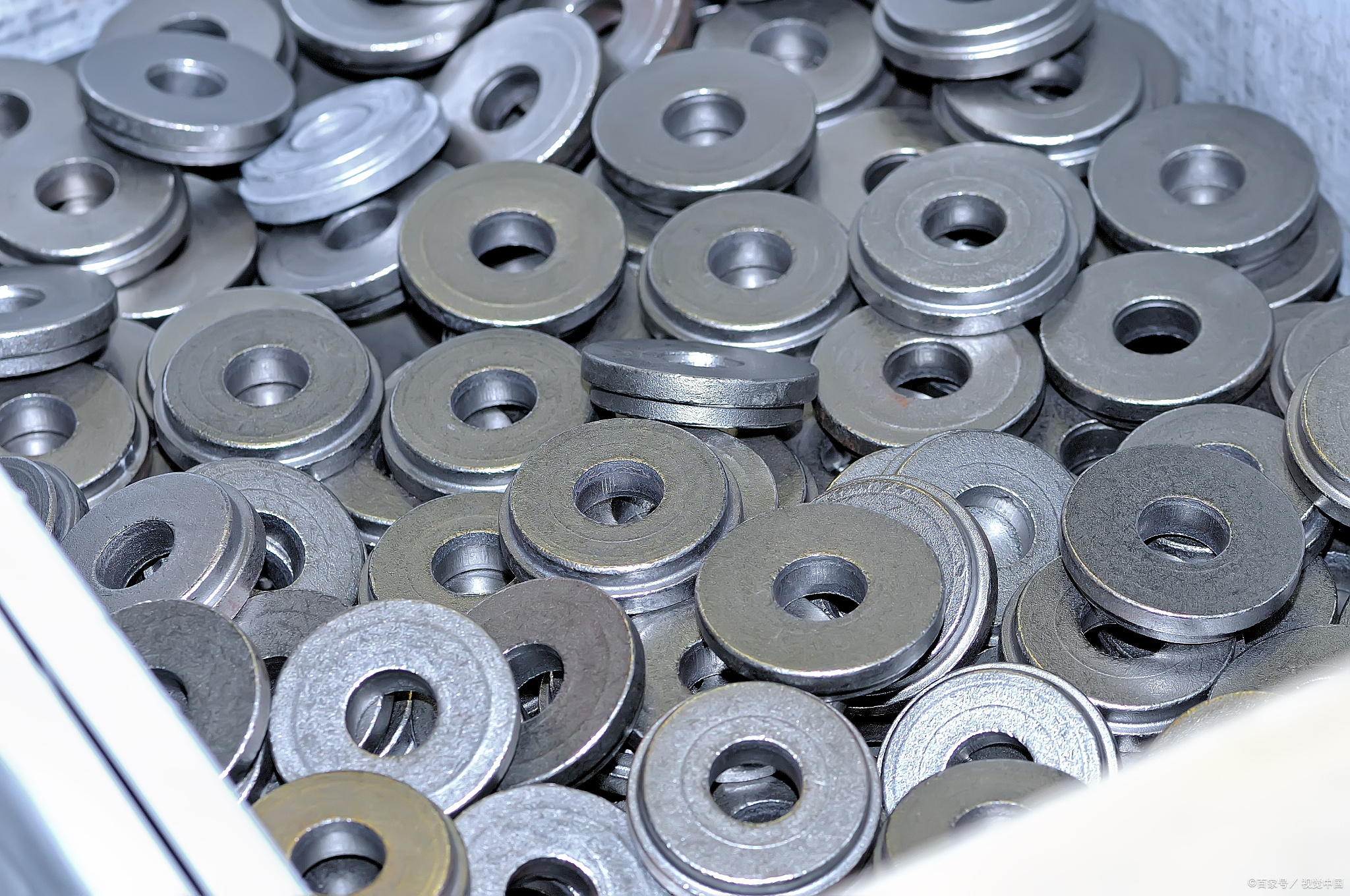

Magnetic Intensity
The information is clear: ferrite magnetic force is usually 800-1000 gauss, and the density is 5(g/cm³). And NdFeB magnetic force in the state of bare magnetism can reach about 3500 Gauss. The density is 7.5(g/cm³).
Thermal Durability
NdFeB is sensitive to temperature, with a Curie temperature of about 310°C to 400°C. If this temperature is exceeded, the magnetic properties of NdFeB are substantially weakened or even lost. If this temperature range is exceeded, the magnetic properties will be greatly weakened or even disappear. Therefore, in the use of such magnets at high temperatures, must take effective heat dissipation measures to ensure its normal operation. Although ferrite magnets do not have as high a magnetic energy product as NdFeB, they have better thermal stability and are able to withstand higher temperatures without losing much of their magnetic properties. This makes ferrite the preferred material for certain applications, such as speaker drive units in high-power audio systems. In these applications, due to the large amount of heat generated during equipment operation, the use of NdFeB could lead to premature failure or performance degradation of the component.
Cost
NdFeB magnets are more expensive, mainly because of the high cost of rare metals such as neodymium, iron and boron. This means that they are more commonly found in high-end audio products. Ferrite magnets are less expensive, simple to manufacture and abundant in raw materials. This makes them more suitable for low-cost or mid-range audio systems.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Advantages: The advantages of ferrite are high magnetic permeability, low cost, high temperature resistance and suitable for low frequency. NdFeB has strong magnetic force and small size, which can give designers more space to design a variety of loudspeakers.
Disadvantages: Ferrite is not as strong as NdFeB. And NdFeB has the disadvantage of poor temperature characteristics and brittleness.

How Should We Choose?
Both neodymium and ferrite magnets have their place in a sound system, and the specifics about which magnet to choose will still depend on what you’re looking for, how much you’re willing to spend, and what kind of sound quality you’re after.
Neodymium magnets are a top choice for some due to their stellar presentation, compact size and lightweight nature. They provide louder and clearer sound reproduction and are particularly suited to application scenarios where space is limited or high mobility is required, such as in-car audio systems.
Ferrite magnets, on the other hand, although slightly less powerful, are a practical choice for applications where size and weight are not an issue, as they are cost effective and still provide satisfactory sound quality.
Anyway, it’s up to you which magnet you choose and what balance you’re looking for. Whichever option you go for, it’s important to make sure your audio system delivers the best possible listening experience. It is also worth remembering that the type and nature of your magnets can have a direct impact on the quality and performance of your sound, so it is worth considering this when choosing.