Your Professional Line Array Speaker Manufacturer
In China, MR AUDIO is a line array speaker OEM manufacturer. We create 400,000 subwoofer sets every year, allowing us to meet your line array speaker requirements.
- Certifications for ISO 9000 quality management systems
- Sets of the assembly line in their entirety
- Warranty of two years
- Excellent research and development, design, and manufacturing systems
Your Line Array Speaker Brand Customization Expert
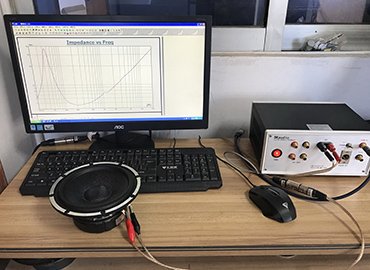
MR AUDIO has made it a priority to design, manufacture, develop, and market a line array speaker. We have advanced testing equipment to ensure that each line array speaker product is of the highest quality.
Our line array speaker is widely used in a variety of sectors all around the world. For all of your line array speaker needs, MR AUDIO is the place to go. Select the types of line array speakers we offer below.
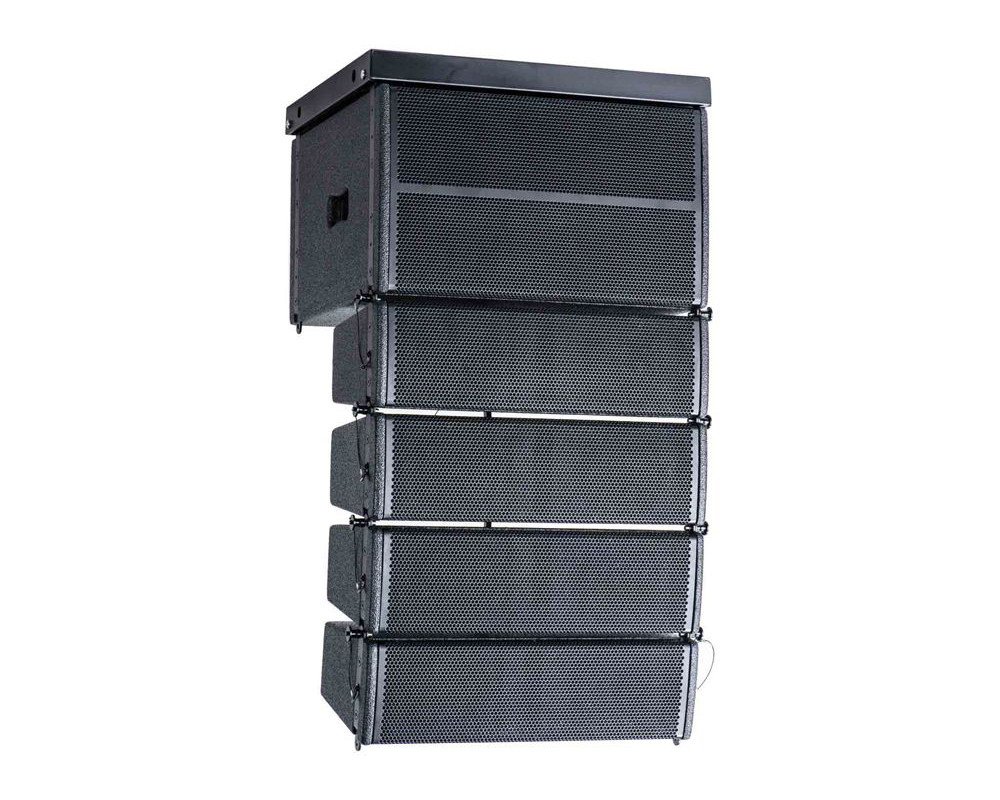
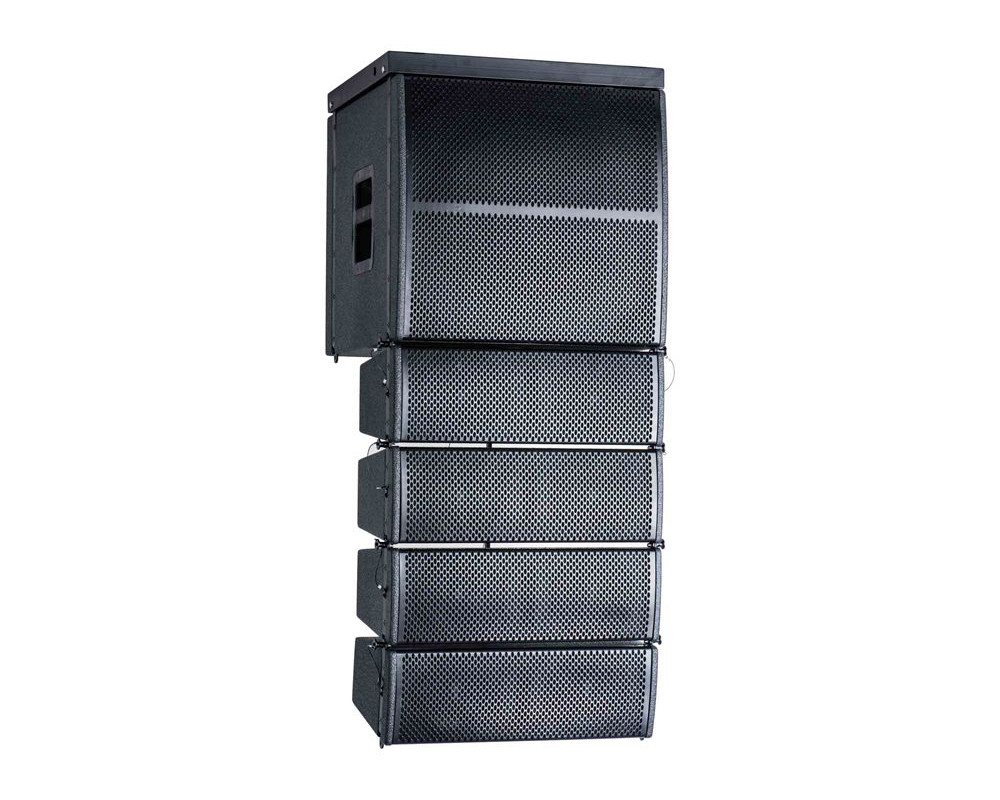
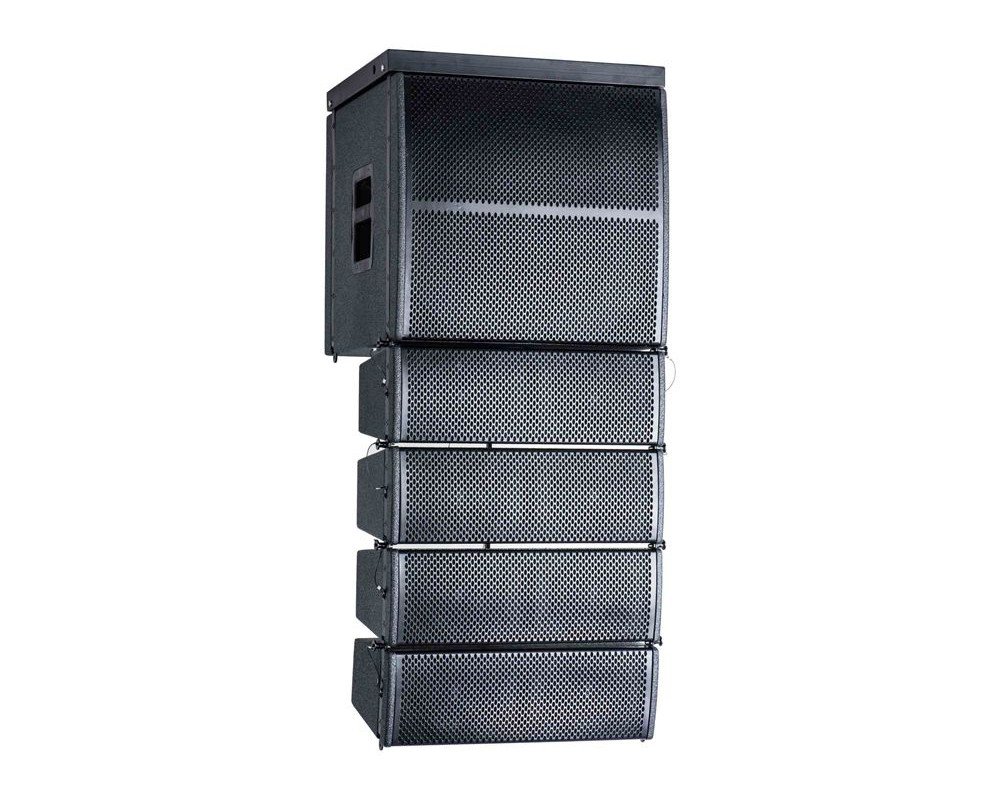
MR Audio Your No.1 Line Array Speaker Manufacturer
- Description: line array speaker
- Nominal Impedance: 16 Ohms
- Rated AES Power Handling(RMS): 400+400 Watts
- Frequency Range: 45-20kHZ
- Sensitivity (1W/1m): 97 dB
- Description:line array speaker
- Nominal Impedance: 8 Ohms
- Rated AES Power Handling(RMS): 400+400 Watts
- Frequency Range: 40-20kHZ
- Sensitivity (1W/1m): 99 dB
- Description:line array speaker
- Nominal Impedance: 16 Ohms
- Rated AES Power Handling(RMS): 800 Watts
- Frequency Range: 55-20KHZ
- Sensitivity (1W/1m): 98 dB
- Description:line array speaker
- Nominal Impedance: 4 Ohms
- Rated AES Power Handling(RMS): 400+400 Watts
- Frequency Range: 45-20kHZ
- Sensitivity (1W/1m):98 dB
- Description:line array speaker
- Nominal Impedance: 8 Ohms
- Rated AES Power Handling(RMS): 400+400 Watts
- Frequency Range: 45-20kHZ
- Sensitivity (1W/1m): 98dB
- Description:line array speaker
- Nominal Impedance: 8 Ohms
- Rated AES Power Handling(RMS): 300+300Watts
- Frequency Range:35-20KHZ
- Sensitivity (1W/1m): 99 dB
What are the features of line arry speakers?
A line array speaker is a group of radiating elements arranged in a straight line and closely spaced, and have the same amplitude and phase.
it is especially suitable for long-distance sound radiation. This is because line array speakers can provide very good vertical coverage directivity to achieve good sound effects.


What advantages do line arry speakers have?
Due to the characteristics of the linear array, the directivity in the vertical plane of the main axis is a narrow beam, and the superposition of energy can radiate long-distance. The lower end of the curved part of the linear column covers the near area, forming a coverage from near to far.
The improvement of the linear array loudspeaker is more in line with the requirements of technology, craftsmanship and installation
MR Audio - Your Professional Line Array Speaker Manufacturer in China


Do you want to get the best Line Array Speaker from China’s best company? MR AUDIO is the one for you. We’ve been working for over 20 years to give the most comprehensive services necessary to increase your business rate.
Our Line Array Speaker features the cutest design and style. It’s available in various sizes to fit your specific speaker’s needs. Can purchase it with the smallest amount of funding.
The most well-known brand in the world awarded the Line Array Speaker the highest honor. We put our expertise to work in offering excellent service through our products.
Customers can get free packaging design for their speakers from MR AUDIO, which is more on their products and markets. We also offer one-stop warehousing, logistics, customs declaration, and customs clearance service.
If you want to include a power amplifier in your business, MR AUDIO is the way to go! Any OEM and ODM services are welcomed with open arms.
You can reach out to us at any time. We hope to create a long-term, mutually beneficial business partnership with you.
MR AUDIO is also available to you 24/7 hours to address all of your needs.

Why Choose MR Audio
- Workshop
- Exhibition Display
- Certificate Display

Recommend Product MR Audio Can Support You
Everything you need to know about line array

A bit of history
Although it appears to be the most recent in sound reinforcement technology, its underlying concepts date back more than 50 years. The first was Auguste Jean Fresnel, who showed a variety of phenomena that may be caused by polarized light in 1814. He noticed that two polarized rays that are placed in the same plane interfere with one another, but they do not interfere when they are perpendicular to one another and are polarized with one another. This finding prompts Einstein to consider that something must occur in a polarized ray perpendicular to the direction of propagation, and it establishes that this something can only be the vibration of the light itself.
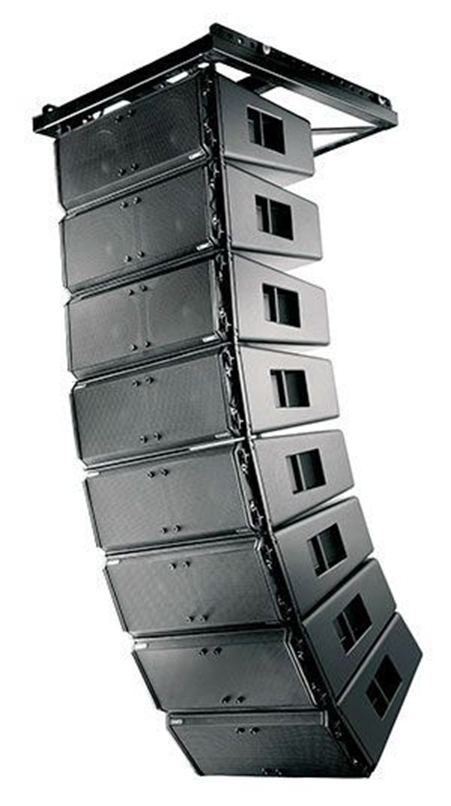

His analogy in the world of sound shows that the reflected and refracted waves are formed by the envelope of elementary waves, produced at the same time at different points on the surface. The reflected ray is perpendicular to the reflected wave, as is the incident ray to the incident wave. From this we can deduce that to avoid considerable lobes in the vertical polar response and that the sum between the individual sound sources has coherence, the maximum separation between boxes has to be less than half the wavelength of the highest frequency that they must reproduce.
Harry F. Olson in his ” Acoustical Engineering “, published in 1947, already advanced various theories applied to acoustics, such as subwoofer lines, arcs, directivity of low frequencies, line arrays, etc.
Technology “WTS” Heil Acoustic
But it wasn’t until the Dr Christian Heil , in 1992, presented in AES (Audio Engineering Society ) the study “Sound sources irradiated by multiple sound sources” when the first line arrays began to be manufactured. This French doctor of acoustics thought that if a stone was thrown into the water, it would cause a progressive circular wave emitted from the point of fall of said stone .
If we throw a handful of stones it would create an interference network . Since the surface of the water does not allow a progressive waveform to be seen, it is as if we are in a chaotic sound field. But it turns out that if we take all those stones, put them in the same bag and throw it into the water, we again observe a progressive circular wave. In other words, what was involved was to create a punctual sound source, in which the opening could be controlled, in order to concentrate the energy on the public area what interests us.
This idea led to the development of the technology WST , wave front Sculpture Technology ( wavefront sculpture) whose objective was to find the physical conditions for a system with several speakers to be the equivalent of a single large sound source, capable of reproducing a continuous and manageable wave. In developing his theory I also observe that the ARF , Active Radiating Factor (active radiation factor) must be greater than 80% of the total area of the complete system, including separation between boxes.
The radiation behavior depends on the ratio between the length of the array and the wavelength of the reproduced frequency. For a fixed frequency, if we increase the length of the line, the main lobe narrows and secondary lobes appear . For a fixed array size, as the frequency increases, the main lobe narrows and secondary lobes appear .
sound propagation
Spherical Waves
As we already know, according to the inverse square law, we have an attenuation of the sound pressure level of 6dB every time we double the distance. This is due to the propagation of sound as a spherical wave front. Thus, every time the distance from the listener to the source is doubled, the radiated energy is dispersed in an area 4 times larger, so the energy density is reduced by a quarter, which means that 6dB drop.
Cylindrical waves
in a line Array, the wavefront generated by each element is cylindrical, remaining constant in the vertical plane. This wave front is almost flat and therefore there are no interferences between each of the sources, so we have a coherent sum behaving like a single sound source.
Difference between near field and far field
propagation the length of the array is not infinite , there will be a point, depending on the frequency, whose resulting wavefront will go from cylindrical to spherical. This point is the one that separates the near field from the far field, so the greater the number of boxes, the farther the near field will reach. If we apply the following formula, we will have the relationship between the length of the array and the limit of the near field:
D = H2f /2C
H= Array height – f = Frequency – c= speed of sound. If the length of the array is 5 m, then if f=100Hz D= 3.7m and if f=1KHz D=37m

Actually the near field behavior of line arrays is more complex. Any given point in the near field is on the axis of only one of the highly directional high-frequency diffusers, but receives low-frequency energy from most of the array components. For this reason, adding more components to the array will increase the low frequency energy in the near field, but the high frequencies will remain the same .
Therefore, line arrays need equalization to boost high frequencies in the far field, equalization effectively compensates for propagation loss. In the near field, it compensates for the constructive sum of the low frequencies and the proximity to the high frequency waveguide.
Array Coverage
The coverage of a system is the angle determined by a 6dB drop in pressure level. for a flat linear array of 2 m its angle of vertical coverage would be:
| If f=100 Hz, lambda = 3.4 m or longitude / lambda = 0.59 on the graph we read > 150º |
| Whereas if f=1KHz, lambda = 0.34 m length / lambda = 5.9 on the graph we read < 15º |
The importance of phase
John Meyer proved the other theory Line Array , where the operating principle of these is much more complex than what was stated above and is a consequence of the phase relationship between the boxes.
A line array it is a group of radiating elements arranged in a straight line, closely spaced and operating with equal amplitude and in phase. Described by Harry Olson in ” Acoustical Engineering “, line arrays are useful in applications where sound must be projected over long distances. This is because line arrays achieve very directional vertical coverage.
Line arrays achieve their directivity by constructive and destructive interference. The directivity of the loudspeaker varies with frequency, at low frequency it is omnidirectional, as the wavelength decreases, as the frequency increases, its directivity narrows. Stacking two of these speakers, one on top of the other, and operating both on the same signal results in a different radiation pattern . At points on the axis between the two there will be constructive interference and the sound pressure will increase by 6 dB relative to the sound pressure of a single unit. At other off-axis points, the differences between the paths will cause cancellations, resulting in a lower sound pressure level. This destructive interference is called ” combing “.
A common misconception about line arrays is that they allow sound waves to combine to create a single cylindrical wave with special propagation characteristics. Under linear acoustics theory, this could not be, so this argument is not science, but a marketing technique.
Sound waves cannot be attached to the sound pressures used in sound reinforcement, but instead pass through each other linearly. Even at the high pressure levels present in the throat of compression drivers, sound waves comply with linear wave theory and pass over each other transparently. Even at pressure levels of more than 130 dB the non-linear distortion is less than 1%.
To check what we just said, we place two boxes on fix ” crossfire “ (crossfire) and we observe in the sound pressure map that one does not affect the other in its axis, as far as coverage and pressure are concerned.
Principles that line arrays must meet
The theory of line array work best for low frequencies. As the wavelength decreases, more and more drivers, smaller in size and more closely spaced , are needed to maintain directivity. The most practical method for PA systems is to use waveguides, diffusers coupled to compression drivers.
Slat emulators and diffusers
A principle that diffusers must meet is to have the smallest possible separation, for which the ideal would be to emulate a slat.
Each manufacturer has chosen a different technique to create their waveguide , thus Christian Heil opted for the DOSC (Spherical and Cylindrical Wave Diffuser). The design of this diffuser allows each sound wave to take the same path, creating a ribbon-shaped wavefront of the same phase from a classic compression driver .
Many other brands, such as Adamson or Nexo, have followed this path with very similar designs . John Mayer opted for a REM tape emulator ( Ruban Manifold Emulator ). In the back of the REM the two motors are placed, while it can be seen how each motor has 4 outputs for its diffusion spaced at less than 2/3 of the wavelength of the maximum frequency reproduced. And oddly enough, many boxes marketed as line array they do not comply with this last principle, although some are already rectifying it .
Line length
Another fundamental principle for the correct operation of a line array is that its length is greater than the wavelength of the minimum frequency that can be reproduced.
Frequency response according to the number of boxes
Another peculiarity is that when stacking boxes these they modify the total frequency response of the system , as we can see in the following graph, where an increase in low and medium frequencies can be seen. The treble frequencies remain unchanged. This characteristic depends on the number of boxes but also on their size .
Frequency response according to environmental parameters
We know that the speed of sound, and therefore its propagation, varies as the temperature does , that is, the more degrees the faster. And that there is also attenuation due to the distance and air absorption . But this is not the only environmental parameter that affects sound, one of the most important is relative humidity, which is measured as a percentage. The interaction of these two factors modifies the frequency response of the system, but only in the treble area.
1. It has uniform coverage and good diffusion. Due to the characteristics of the line array, the directivity in the vertical plane of the main axis is a narrow beam, and the energy superposition can be radiated over a long distance. The lower end of the curved part of the linear column covers the near area, forming a coverage from near to far.
2. The improvement of the line array loudspeaker is more in line with the requirements of technology, craftsmanship and installation.
3. The sound pressure level is large.
4. Strong directivity The difference between the far and near fields is small.
5. On-site installation and hanging are convenient.
Surface mounted, normal installation, hoisting these methods.
1. Surface installation: refers to installing the speaker system directly in the visible place in the hall;
2. Concealed installation: refers to the installation of the speaker system on the wall, frame, or flat roof;
3. Hoisting: As the name implies, it refers to the use of hooks and baskets to directly hang the speakers on the ceiling wall.
1.There should be no obstacles between the sound and the audience, and should not be blocked. The audience should be directly radiated to minimize the loss of sound.
2. It is necessary to ensure that all points in the auditorium can obtain uniform direct radiation.
3. The speaker needs to be firmly fixed to avoid falling and hurting people due to vibration. i.e. ensure safety.
4. When installing the speaker system, the modeling structure of the entire hall should be considered, and try to avoid the installation of speakers and damage to the beauty of the entire structure.
1. The installation holes reserved in advance should be large enough, because the installation angle of the speaker should also be considered.
2. If it is installed in the ceiling, there are two ways to install the line array speaker system. The first is to install the speaker in the echo cover of the ceiling to avoid the attenuation of sound energy caused by sound escape. The sound enclosure should be made of hardwood and be securely fastened to avoid damaging the sound quality due to resonance. Another way is to place it parallel to the ceiling, and now the sound is directed towards the auditorium. This way is more suitable for the venue sound supply system of the stadium, the bass speaker system and the distributed background sound supply system.
3. The mask used for concealed installation should be sound transparent.
4. The best decorative lattice should be wedge-shaped and the width should be less than one-fifth of the radius of the speaker cone, and the opening ratio of the lattice should be >=75% to facilitate the spread of sound.
5. Compared with exposed installation, concealed installation can avoid damaging the decoration style of the hall, but due to the complicated installation and improper handling, it will cause sound attenuation and affect the effect. Moreover, it is also complicated and troublesome to adjust and maintain.
1. When determining the hoisting position and angle, the focusing area of the main sound beam of the speaker and the sound field distribution of the entire hall should be considered.
2. Security issues. Be sure to install it firmly to avoid falling and hurting people.
The configuration of the line array audio depends on the frequency division of the audio. The things required for the external frequency division and the built-in frequency division are different, and the 2-frequency, 3-frequency, and 4-frequency divisions are also different.
There are air boxes (for speakers), field frames (for hanging speakers), chain hoists or electric hoists (for lifting speakers). If the line array is multi-frequency, you need multi-core speaker cables (2-frequency 4 core, 3-frequency 6-core), a supporting power amplifier, audio processor, and mixer.