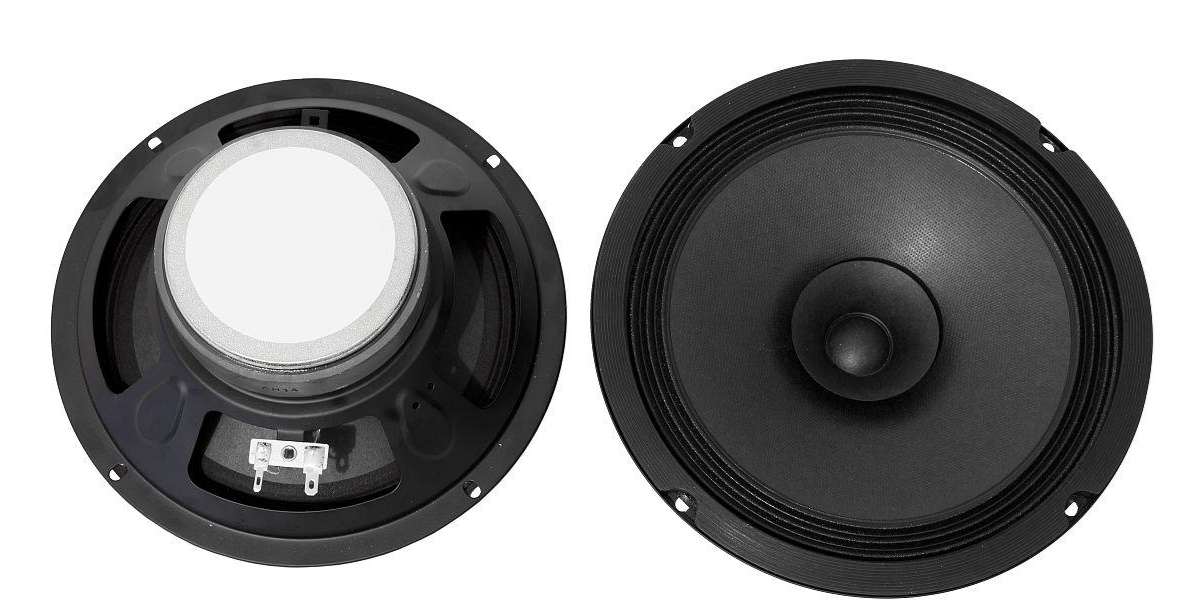
Tweeter design has a significant impact on sound, affecting the audio’s frequency response, directivity, distortion, and the overall quality of the sound.
When selecting a tweeter, it’s crucial to have a crossover point in mind. For example, in a 6.5-inch two-way speaker, the common crossover point falls between 2-4 kHz, with 2.5 kilohertz being a common choice. To ensure a smooth transition between the tweeter and mid-woofer, the tweeter’s working frequency band should be lower than the crossover point.
Ideally, it should be approximately double the frequency, ensuring a natural frequency division. Additionally, the tweeter’s resonant frequency should be lower than 1.25 kHz, although some tweeters on the market have a resonant frequency exceeding 2 kHz, which can lead to frequency crossover issues and unnatural response curves.
To assess a tweeter’s suitability, one must consider its cut-off frequency. By understanding the relationship between the tweeter’s diaphragm behavior and its resonant frequency, you can determine its effective working frequency band, typically governed by the tweeter’s resonant frequency (F0).
Impact of Tweeter Design:
Frequency Response: A tweeter’s design, including diaphragm material, diameter, and driver unit structure, significantly affects its ability to reproduce high-frequency sounds efficiently. A good tweeter should produce clear highs with a flat frequency response and minimal flutter or distortion.
Directivity: Tweeter design elements like parabolic reflectors, waveguides, speaker apertures, and shapes influence the sound’s radiation pattern at different angles, ensuring a consistent listening experience at various locations.
Distortion: Tweeter design plays a crucial role in managing distortion, including harmonic, intermodulation, and phase distortion. Proper materials and construction can reduce distortion and enhance sound purity and accuracy.
Power Handling: Tweeters must be capable of handling input power to prevent damage or distortion from overloading. Factors like cooling systems and driver unit materials impact power handling capabilities.
Speaker Cabinet Design: Tweeters are typically integrated into speaker cabinets. Cabinet design influences the sound field, sound pressure level, and overall sound quality, particularly for low-frequency response and resonance reduction.
Tweeter Location: The positioning and orientation of the tweeter within the speaker or sound system are critical factors affecting sound quality. Consideration must be given to optimize tweeter placement and direction for the best results.
In summary, tweeter design involves a delicate balance of multiple factors to deliver a clear, accurate, and enjoyable audio experience. Different applications and environments may require specific design considerations to meet particular sound requirements.